Dislocker is an open source software used to mount and access (read or write) BitLocker encrypted drives on Linux and Mac, it uses a Fuse (another open source software) based mechanism to decrypt BitLocker encrypted drives and mount the drives so that the user can access the files within the drives. When using dislocker to mount drives, the user needs to provide a valid BEK file (startup key), numerical key, FVEK (Full Volume Encryption Key), recovery password or password, so it is not a brute force mechanism or hack.
Dislocker is a free and open source command tool which allows you to mount and access BitLocker encrypted drives in Linux and Mac, it's complex and therefore difficult for non-professionals to use, fortunately there is an alternative to dislocker - BitLocker Anywhere For Linux, which provides an easy-to-use graphical user interface to help you easily mount and access BitLocker encrypted drives on Linux.
Please note that to access BitLocker encrypted drive in Linux, Hasleo BitLocker Anywhere For Linux requires a healthy Bitlocker encrypted drive. If your Bitlocker encrypted drive is corrupted, please try the best Bitlocker data recovery software Hasleo BitLocker Data Recovery to recover files from a damaged or corrupted BitLocker encrypted drive.
How to install dislocker on Linux?
For Debian-like: apt-get install libfuse-dev libpolarssl-dev
For Fedora-like: yum install fuse-devel polarssl-devel
How to use dislocker on Linux?
After installing dislocker on Linux, please run dislocker on the command line to see how to use it.
Usage: dislocker [-hqrsv] [-l LOG_FILE] [-o OFFSET] [-V VOLUME DECRYPTMETHOD -F[N]] [-- ARGS...] with DECRYPTMETHOD = -p[RECOVERY_PASSWORD]|-f BEK_FILE|-u[USER_PASSWORD]|-k FVEK_FILE|-c
Options:
-c, --clearkey decrypt volume using a clear key (default)
-f, --bekfile BEKFILE decrypt volume using the bek file (on USB key)
-F, --force-block N force use of metadata block number N (1, 2 or 3)
-h, --help print this help and exit
-k, --fvek FVEK_FILE decrypt volume using the FVEK directly
-l, --logfile LOG_FILE put messages into this file (stdout by default)
-o, --offset OFFSET BitLocker partition offset (default is 0)
-p, --recovery-password[RECOVERY_PASSWORD] decrypt volume using the recovery password method
-q, --quiet do NOT display anything
-r, --readonly do not allow to write on the BitLocker volume
-s, --stateok do not check the volume's state, assume it's ok to mount it
-u, --user-password decrypt volume using the user password method
-v, --verbosity increase verbosity (CRITICAL errors are displayed by default)
-V, --volume VOLUME volume to get metadata and keys from
-- end of program options, beginning of FUSE's ones
ARGS are any arguments you want to pass to FUSE. You need to pass at least the mount-point.
Step 1. Download and extract Hasleo BitLocker Anywhere For Linux.
Step 2. Open a terminal as a non-root user, go to the bin subfolder under the extract folder, then execute the 'run.sh' script to start the program.
Step 3. Right-click the BitLocker encrypted drive you want to access in main window, then click "Mount drive".
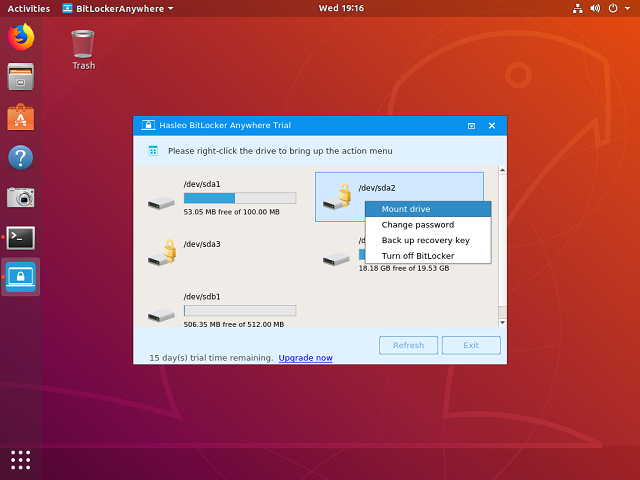
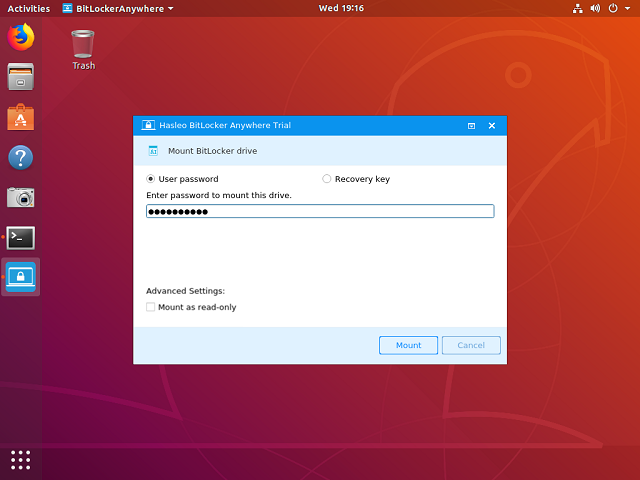
Step 4. Enter the password or recovery key, then click "Mount" button to mount the drive.
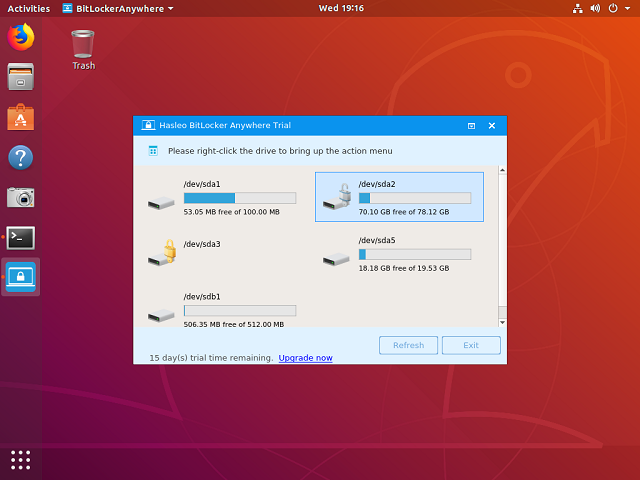
Step 5. After the operation completes successfully, the drive has been successfully mounted. Please note that the default mount path for the drive is: /mnt/BitLockerAnywhere/xxxx (xxxx is the device name of the device.).
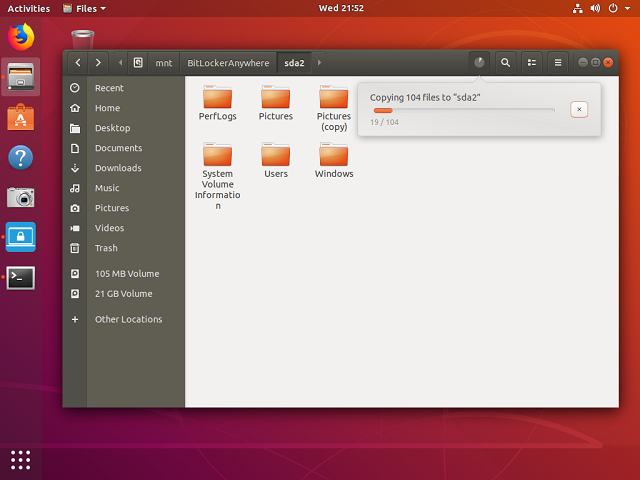
Step 6. Now you can full read and write access to the BitLocker encrypted drive as access a Linux's native drive, such as read, write, copy, delete files, etc.
As you can see, dislocker is an open source software which you can use it to mount and access Bitlocker encrypted drives on Linux. And BitLocker Anywhere For Linux is an alternative to dislocker, it provides a graphical user interface and is therefore easier for us to use.
As a ALL-IN-ONE BitLocker Solution for Linux, we can also use BitLocker Anywhere For Linux to encrypt drives with BitLocker in Linux or decrypt drives with BitLocker in Linux.