You should have realized the importance of backing up data, which is why you choose to use backup software. You know that the data on our computers changes every day, and if you forget to back up important data because you're too busy at work, you may lose important data in the event of a disaster. To prevent this from happening, automatically perform backup task on a regular basis is a good solution.
Hasleo Backup Suite supports the creation of complex backup schedules to automatically and regularly perform a backup task, which can be accomplished through a mix of one-time, daily, weekly, monthly or event-triggered backup scheduling combined with the image retention policy. Below we will describe how to add, edit, and delete backup schedules, and how to configure the image retention policy.
Click "Add backup schedule" and select the schedule type (One-time, Daily, Weekly, Monthly or Event Trigger) in the pop-up window, then complete the settings according to the selected scheduling type (please refer to the description below), and finally click OK to save the settings.
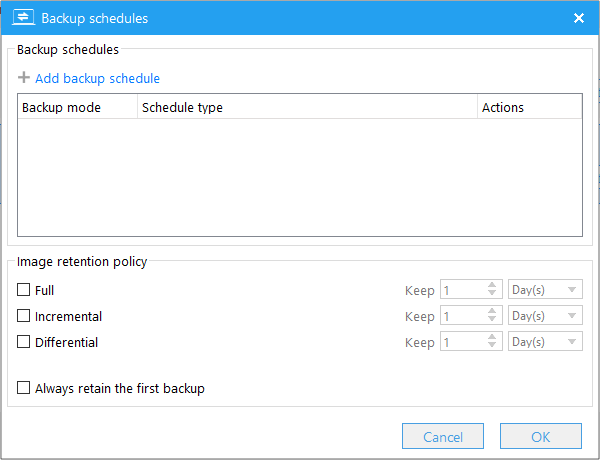
Perform the backup task once at the certain time.
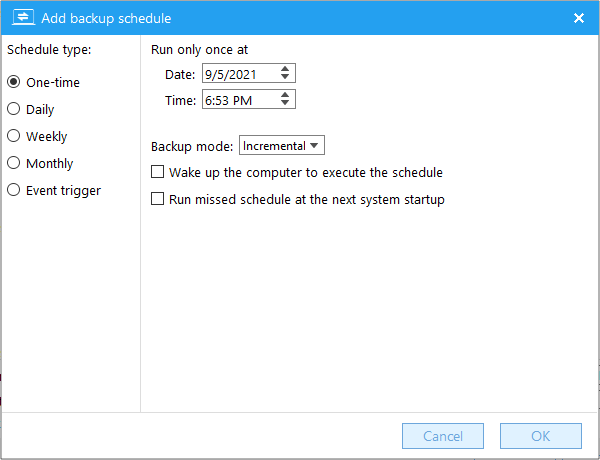
The backup task is automatically performed once at a certain time each day, or the backup task is performed periodically at a certain time interval within a time period of each day.
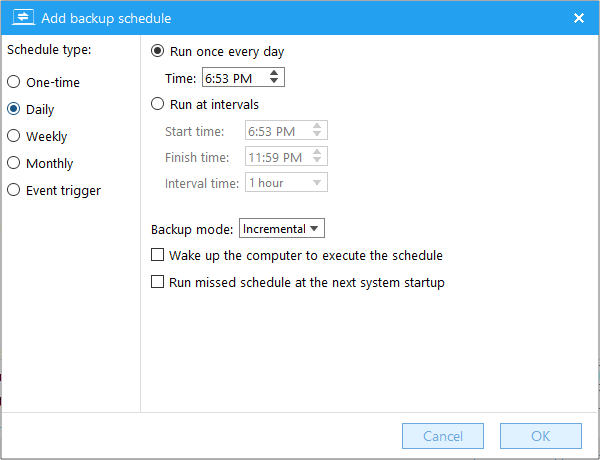
Perform the backup task once at the certain time on certain day(s) of each week.
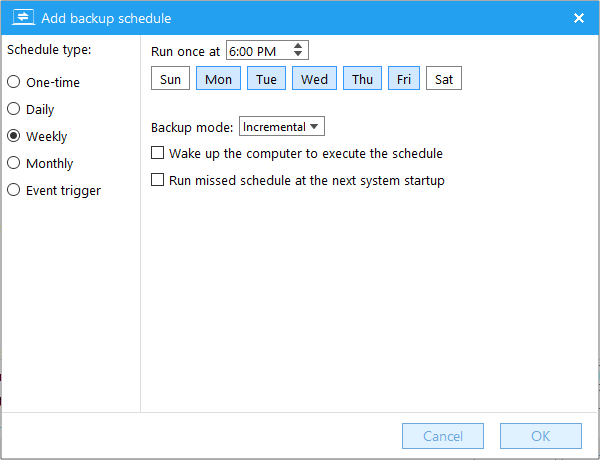
Perform the backup task once at the certain time on certain day(s) of certain month(s).
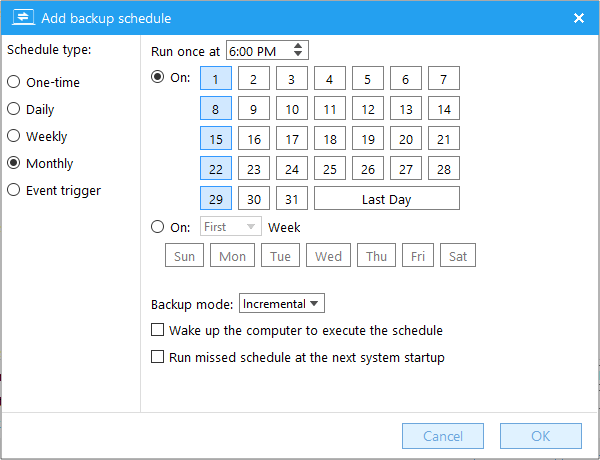
Perform the backup task when the specified event occurs.
Backup mode: The type of backup generated when the backup schedule is executed.
Wake up the computer to execute the schedule: Wake up the computer to perform the task when the computer is in hibernation or sleep state.
Run missed schedule at the next system startup: Perform the backup task that has been missed when the Windows system starts.
Run only once a day: Perform the backup task only once a day even if the specified event occurs multiple times.
Notes: If multiple schedules of a task are set to generate backups at the same time, Hasleo Backup Suite will only generate one backup (The hierarchy of Full over Differential over Incremental will be respected.), because it does not make much sense to generate multiple backups continuously in a short period of time.
Click the ![]() icon on the right side of the backup schedule or double-click the backup schedule you want to edit, then make changes as needed in the pop-up window, and finally click "OK" to save the changes.
icon on the right side of the backup schedule or double-click the backup schedule you want to edit, then make changes as needed in the pop-up window, and finally click "OK" to save the changes.
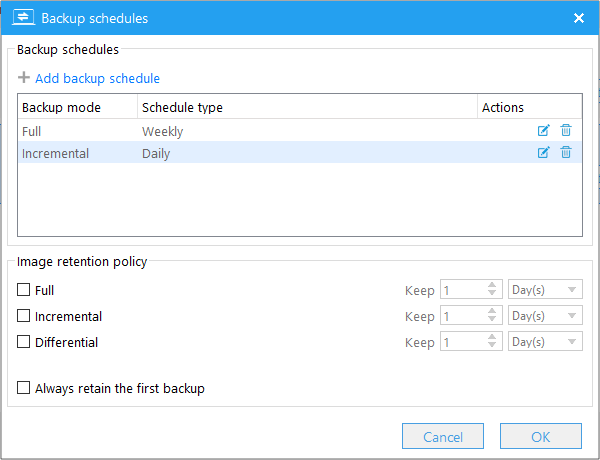
For more information on how to set up backup schedules, please refer to the Add backup schedule section on this page.
Click the ![]() icon on the right side of the backup schedule you want to delete, and then click the "Yes" button in the pop-up message box to confirm the deletion.
icon on the right side of the backup schedule you want to delete, and then click the "Yes" button in the pop-up message box to confirm the deletion.
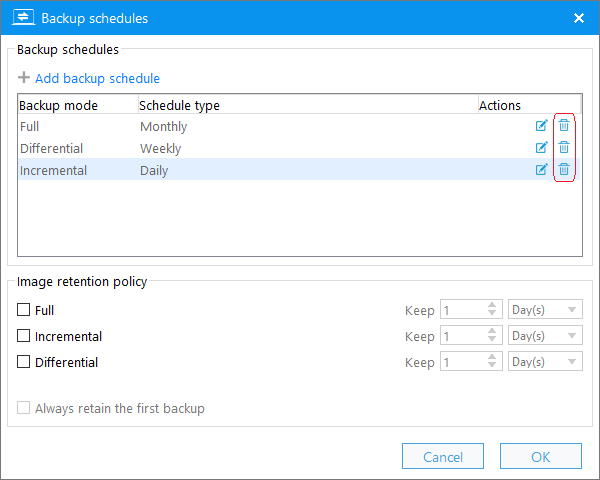
The image retention policy is used to determine how long or how many each type of backup image files should be retained for a backup task, which makes it easier for you to manage the storage space used by a backup task. For more information about the image retention policy, see the detailed explanation below.
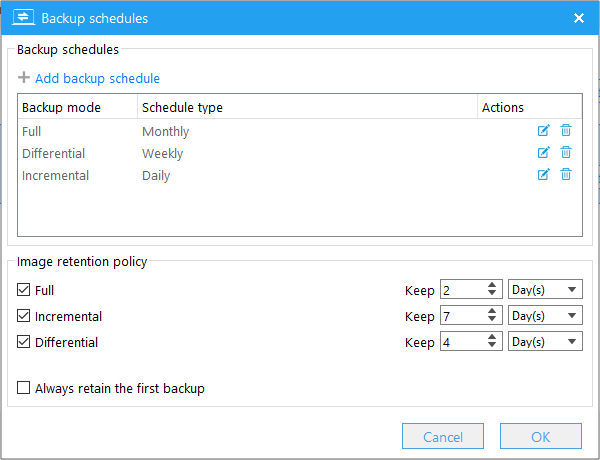
Always retain the first backup: We recommend that you always tick this option, because the first backup of the task is always a full backup, and it is time-consuming to merge a full backup with other backups. Please note that if this option is checked, the first backup image of the backup task will be excluded from the image retention policy.
1. Since it usually takes a long time to merge image files, Hasleo Backup Suite now uses both image deletion and image merge methods to implement image retention policy to improve efficiency.
2. When deleting full backups, all differential and incremental backups linked to those full backups are also deleted.
3. When deleting differential backups, all incremental backups linked to those differential backups are also deleted.
4. When deleting incremental backups, use both image deletion and image merge methods to ensure that the backup chain is not broken. Please note that in the examples below, F refers to a full backup, D refers to a differential backup, and I refers to an incremental backup.
(4.1) Example 1, before retention, there is a backup chain F I I F I I I, and the image retention policy is set to retain three incremental backups, we only need to delete the first two incremental backups, because there are no other backups linked to these incremental backups, and deleting them will not cause the backup chain to break.
(4.2) Example 2, before retention, there is a backup chain F I I F I I I, and the image retention policy is set to retain two incremental backups, we can safely delete the first two incremental backups, but we cannot delete the third incremental backup, because the last two incremental backups are linked to the third incremental backup. The solution is to merge the third incremental backup with the fourth incremental backup to produce a new incremental backup.
5. Since the image files are deleted directly, it is normal to warn that the image files have been deleted or lost when checking the integrity of the backup image files.