This tutorial describes how to use Hasleo Backup Suite to restore an MBR system backup image to a GPT disk. It also covers key concepts for this specific restoration scenario.
MBR (Master Boot Record): First introduced in 1983 with IBM PC DOS, the MBR defines the partition table layout on a hard drive. It is located in the disk's first sector (LBA 0 or CHS 0/0/1) and consists of boot code, a disk signature, a partition table, and an end flag. Its specific structure is as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x000 | 440 | Boot code (flat binary executable code) |
| 0x1B8 | 4 | Unique disk signature |
| 0x1BC | 16 | First partition table entry |
| 0x1CC | 16 | Second partition table entry |
| 0x1DC | 16 | Third partition table entry |
| 0x1EC | 16 | Fourth partition table entry |
| 0x1FE | 2 | End flag(0x55, 0xAA) |
MBR uses partition table entries to describe disk partitions; the structure of a partition table entry is as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 1 | Drive attributes (0x80: active partition) |
| 0x01 | 3 | CHS Address of partition start |
| 0x04 | 1 | Partition type |
| 0x05 | 3 | CHS address of last partition sector |
| 0x08 | 4 | LBA of partition start |
| 0x0C | 4 | Number of sectors in partition |
Since the CHS addressing method can only access disks no larger than 7.844 GB, operating systems nowadays typically use the LBA addressing method to access disks, and we see only 4 bytes of LBA in the partition table entries of the MBR, so this results in the MBR partition scheme only accessing disks up to 2 TB (2 ^ 32 x 512) in size.
GPT (GUID Partition Table): It is a part of the EFI standard that defines the partition table layout on a hard drive. It uses LBA addressing in place of the historical CHS addressing, mainly designed to replace the MBR partition scheme used by legacy BIOS computers. On a GPT disk, the partition table's location information is stored in the GPT header. For compatibility with older systems, the first sector of the hard disk remains a MBR (Protective MBR). The overall disk structure, in order, is: the Protective MBR, the primary GPT header, the primary partition table, the actual partitions, the backup partition table, and GPT header. The specific structure is as follows:
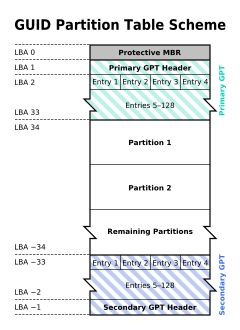
✦ Protective MBR: There is a partition table entry with partition type 0xEE in the Protective MBR of the GPT disk, which is used to distinguish whether it is a GPT disk or a MBR disk.
✦ Primary GPT header: The primary GPT header stores information such as the unique disk GUID (used to uniquely identify a GPT disk), CRC (cyclic redundancy check) of GPT header and partition table, the number of partition table entries, and the start LBA of the partition table entries array.
✦ Partition table entry: It is used to describe a partition on the disk, including the partition GUID, start LBA and end LBA, as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 16 | Partition type GUID |
| 0x10 | 16 | Unique partition GUID |
| 0x20 | 8 | First LBA |
| 0x28 | 8 | Last LBA |
| 0x30 | 8 | Attribute flags (read-only, hidden, etc.) |
| 0x38 | 72 | Partition name |
✦ Backup partition table and GPT header: They are backups of the primary partition table and GPT header, used to restore GPT if the primary partition table or GPT header is lost or corrupted.
Compared to the MBR partition scheme, GPT partition scheme has more advantages.
| MBR | GPT | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum disk capacity | 2 TB | 9.4 ZB (9,400,000,000 TB) |
| Maximum partition capacity | 2 TB | 9.4 ZB (9,400,000,000 TB) |
| Maximum number of partitions | 4 primary partitions and several logical partitions | Unlimited number of primary partitions, Windows limits it to 128 partitions |
| Firmware boot support | BIOS | UEFI |
| Data read or write support | All Windows operating systems | 32-bit Windows Vista and later64-bit Windows XP and later |
✦ 1. GPT breaks the limitation of MBR on disk and partition capacity: GPT supports larger partition and disk capacities, with a maximum of 9.4ZB of partition and disk capacity.
✦ 2. GPT disk can be used as boot device for UEFI-based computers: As modern computers typically use UEFI firmware, which requires the GPT partitioning scheme for booting and is part of the UEFI standard, GPT is becoming the future trend.
✦ 3. GPT partition scheme is more secure: The GPT header contains a CRC check that can be used to determine whether the GPT header and the partition table are damaged, and there are backups of the GPT header and the partition table, so if the primary GPT header or the partition table is lost or damaged, it can be restored from the backup.
✦ 4. Windows 11 can only be installed to a GPT disk: Since Windows 11, Microsoft has mandated that Windows 11 must be installed on UEFI computers, which means we have to use GPT to install and run Windows 11.
If you have bought a new UEFI-based computer and want to transfer your entire Windows environment from your old computer without reinstalling or configuring anything. Or you accidentally installed Windows in Legacy BIOS (MBR) mode on a UEFI-based computer (some UEFI computers are still compatible with Legacy BIOS mode. For more detailed information about Legacy BIOS and UEFI, please refer to Legacy BIOS VS UEFI), and want to run it in true UEFI mode. Below we'll describe how to back up Windows operating system and then restore MBR system image to GPT disk.
Step 1. Download, install and run Hasleo Backup Suite. If you do not have a Windows backup image, please make a backup image for your Windows operating system first.
Step 2. Click the "Restore" button in the navigation bar. Click "Browse image to restore" in the operation area. From the open file dialog box, select the system backup image file you want to restore.
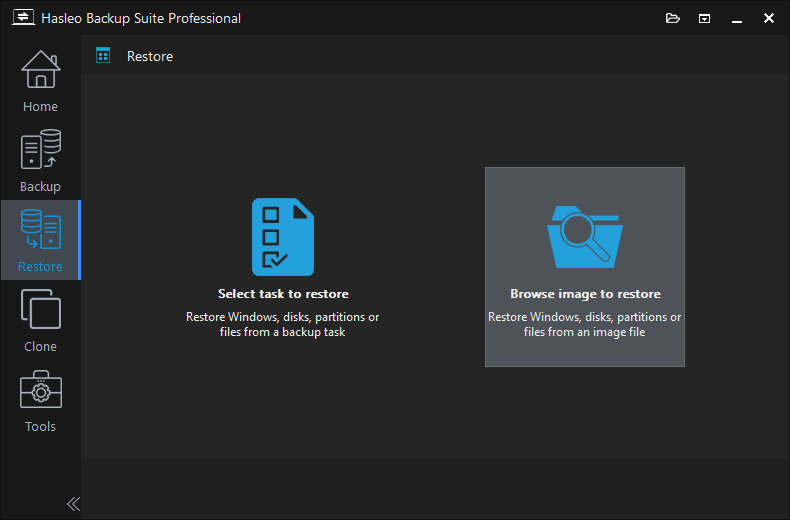
Step 3. Select the backup version you want to restore, click "System mode", and then click the "Next" button.
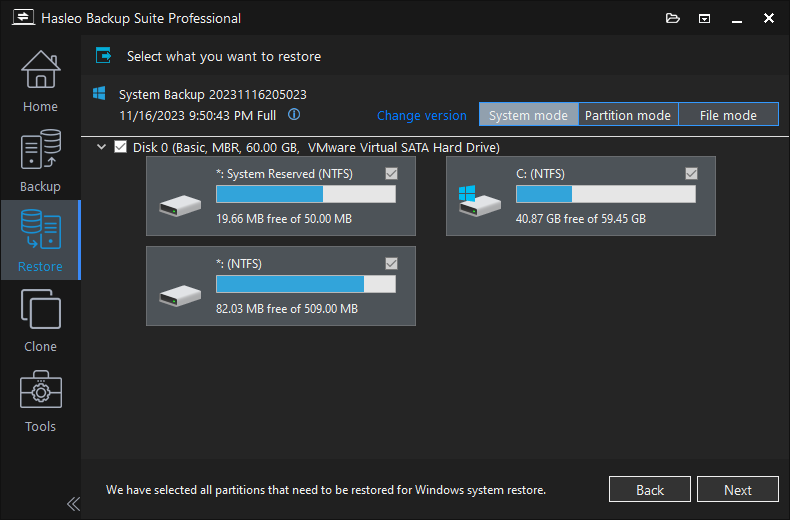
Step 4. Select the destination disk you want to restore the Windows operating system to, and check the "Restore as GPT" checkbox, then click "Next".
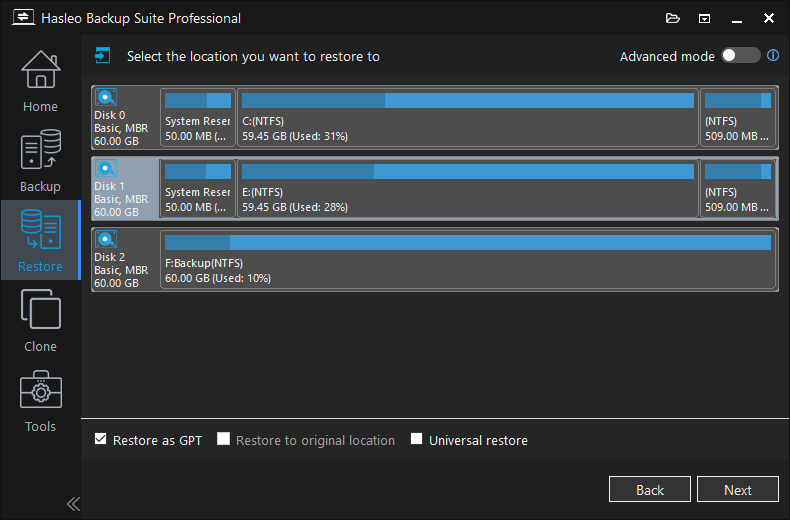
Step 5. Adjust the size and location of the partitions as needed, then click "Proceed". A warning message may pop up to tell you that all data on the destination drive will be destroyed. Click "Yes" to continue if you have no important data on the destination disk. Please note that if you choose to restore Windows to the original disk, Hasleo Backup Suite needs to be restarted into a Pre-OS environment to complete the clone operation. Just follow the prompts.
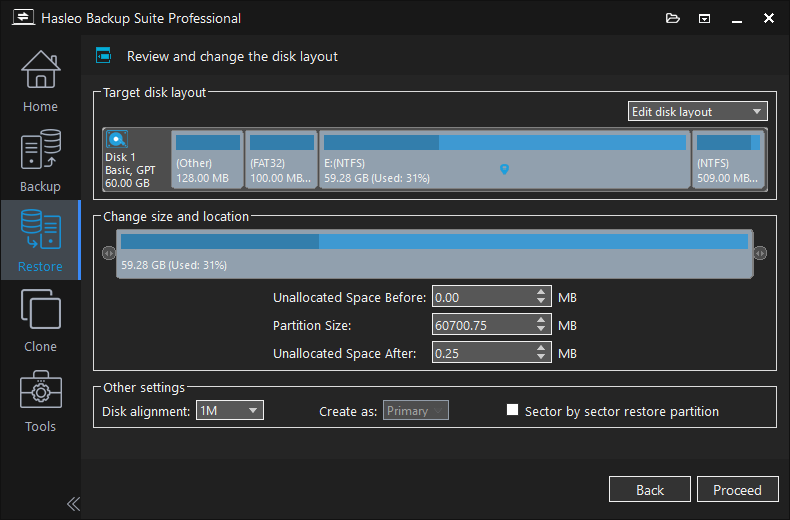
Step 6. Hasleo Backup Suite began restoring the Windows operating system to the destination disk. Please note that the time required for restore operation is related to the size of the data that needs to be restored, so please be patient.
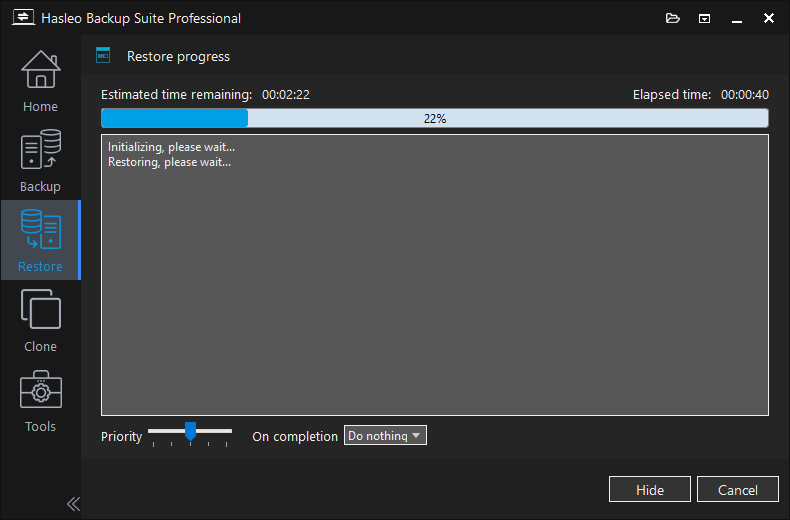
Step 7. After the clone operation is complete, restart the computer and change the boot sequence to boot from the destination disk in UEFI mode.
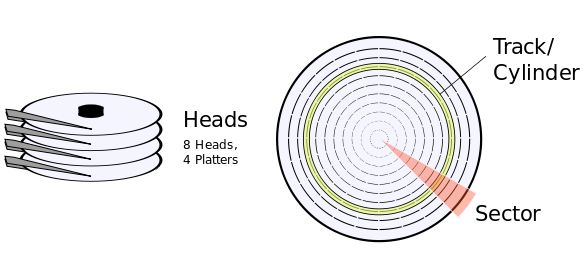
✦ Head: A mechanical hard disk usually consists of multiple platters, and each platter usually has two heads (one on the front and one on the back of the platter), so a disk with four platters usually has eight heads as shown in the figure below. Heads are numbered from 0 and the valid range is between 0 and 254.
✦ Cylinder: A platter is divided into multiple concentric rings from the inside to the outside, which we call tracks. All platters of the same hard disk have the same number of tracks. The tracks with the same track number on all platters are called cylinder. Cylinders are numbered from 0, the valid range is between 0 and 1023.
✦ Sector: All tracks on a disk are divided into the same number of units, which we call sectors, and the size of all sectors on a disk is the same, usually 512 bytes. Please note that all tracks on a platter have the same number of sectors, even though tracks on the periphery of the platter could theoretically have more sectors. Sectors in a track are numbered from 1, the valid range is between 1 and 63.
After knowing the number of cylinders, the number of disks and the sector size of a disk, we can calculate the capacity of a disk in the following way:hard disk capacity = number of cylinders × number of head × number of sectors per track × bytes per sector
If you are a computer hobbyist, you may have heard of the CHS (Cylinder-Head-Sector Addressing) and LBA (Logical Block Addressing) addressing methods for hard drives.
✦ CHS: As mentioned earlier, every sector on a disk can be located using its cylinder, head, and sector number. However, because each of these values has a defined maximum, the CHS method can only address disks up to 7.844 GB.
✦ LBA: For hard disks larger than 7.844 GB, the CHS addressing method obviously cannot address all sectors. Consequently, the Logical Block Addressing (LBA) method was introduced to solve this problem. LBA works by sequentially numbering all disk sectors starting from 0, thereby eliminating the capacity limitations of CHS. However, for compatibility reasons (particularly during system boot), CHS addressing still needs to be supported, which we won't discuss here.
This tutorial describes how to use Hasleo Backup Suite to restore an MBR system backup image to a GPT disk. It also introduces some knowledge related to this process, such as hardware physical structure, CHS and LBA addressing methods, MBR vs. GPT differences, and the advantages of GPT.
As professional Windows backup and cloning software, Hasleo Backup Suite enables you to not only restore an MBR system backup image to a GPT disk, but also restore a GPT system backup image to MBR disk.