This tutorial explains how to clone Windows from a GPT disk to an MBR disk using Hasleo Backup Suite, as well as key concepts for this process.
The Master Boot Record (MBR) was introduced with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It is called "Master Boot Record" because it is a special boot sector located at the beginning of a drive, containing the operating system's boot loader and the drive's partition table. The specific structure is as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x000 | 440 | Boot code (flat binary executable code) |
| 0x1B8 | 4 | Unique disk signature |
| 0x1BC | 16 | First partition table entry |
| 0x1CC | 16 | Second partition table entry |
| 0x1DC | 16 | Third partition table entry |
| 0x1EC | 16 | Fourth partition table entry |
| 0x1FE | 2 | End flag(0x55, 0xAA) |
As shown above, an extended partition uses an Extended Boot Record (EBR) to describe its logical partitions. The previous EBR points to the next one, so multiple partitions can be described, which are called logical partitions.
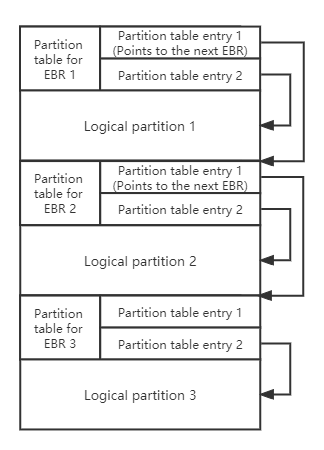
As shown above, the extended partition use the Extended Boot Record (EBR) to describe partitions, the previous EBR points to the next EBR, so multiple partitions can be described, which are called logical partitions.
The MBR uses partition table entries to describe the partitions on the disk; the structure of a partition table entry is as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 1 | Drive attributes (0x80: active partition) |
| 0x01 | 3 | CHS Address of partition start |
| 0x04 | 1 | Partition type |
| 0x05 | 3 | CHS address of last partition sector |
| 0x08 | 4 | LBA of partition start |
| 0x0C | 4 | Number of sectors in partition |
We can see that the partition table entry uses 4 bytes to describe the starting sector number and number of sectors of the partition, so MBR can only address disks up to 2 TB (2 ^ 32 x 512).
GUID Partition Table (GPT), a part of the EFI standard, defines the layout of the partition table on a drive. With the rapid growth of hard disk capacities, the MBR partitioning scheme—limited to describing only four primary partitions and 2.2TB of space—became inadequate. To solve these problems, GPT came into being. The promotion of UEFI BIOS provided a solid technical foundation for GPT. In GPT, all partition information is stored in the GPT header. The first sector of the disk uses a structure identical to MBR, known as the Protective MBR, which allows an operating system to identify whether a disk is formatted with MBR or GPT. The structure of the GPT is as follows:
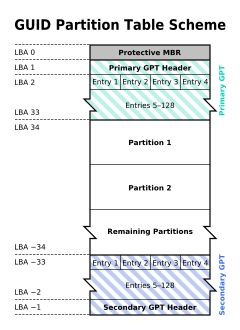
✦ Protective MBR: A GPT disk contains a partition table entry with type 0xEE in its Protective MBR, which is used to distinguish whether it is a GPT disk or a MBR disk.
✦ Primary GPT header: The primary GPT header stores information such as the unique disk GUID (used to uniquely identify a GPT disk), CRC (cyclic redundancy check) of GPT header and partition table, the number of partition table entries, and the start LBA of the partition table entries array.
✦ Partition table entry: It is used to describe a partition on the disk, including the partition GUID, start LBA and end LBA, as follows:
| Offset | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 16 | Partition type GUID |
| 0x10 | 16 | Unique partition GUID |
| 0x20 | 8 | First LBA |
| 0x28 | 8 | Last LBA |
| 0x30 | 8 | Attribute flags (read-only, hidden, etc.) |
| 0x38 | 72 | Partition name |
✦ Backup partition table and GPT header: They are backups of the primary partition table and GPT header, used to restore GPT if the primary partition table or GPT header is lost or corrupted.
Having detailed MBR and GPT, it is very clear that GPT has greater advantages than MBR. So, when would you need to convert a Windows system from GPT to MBR? The primary scenario is when cloning a Windows installation from a modern UEFI-based computer to run on a legacy BIOS-based computer, as BIOS requires the MBR partition style for booting.
Step 1. Download, install, and run Hasleo Backup Suite.
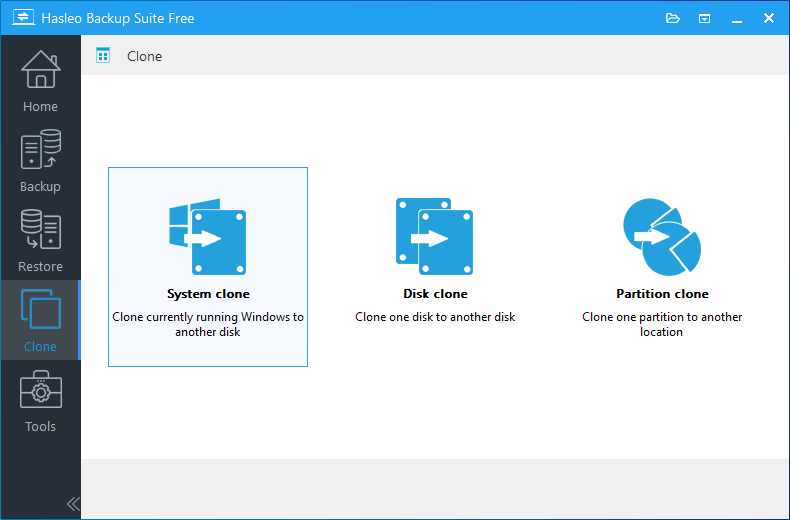
Step 2. Click the "Clone" button in the navigation bar, then click "System clone" button in the operation area.
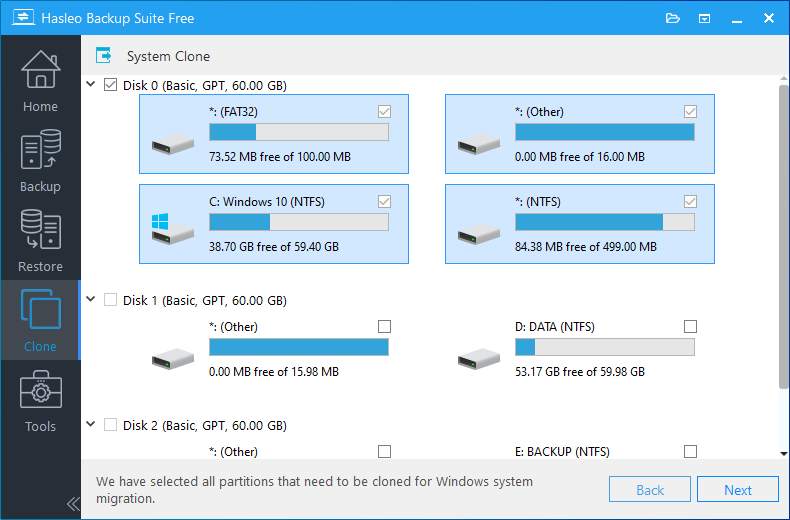
Step 3. Hasleo Backup Suite will automatically select all partitions required for a Windows system clone. Simply click "Next" to proceed.
Step 4. Select the destination disk to which you want to clone the Windows OS. Tick the "Clone as MBR" option, then click "Next".
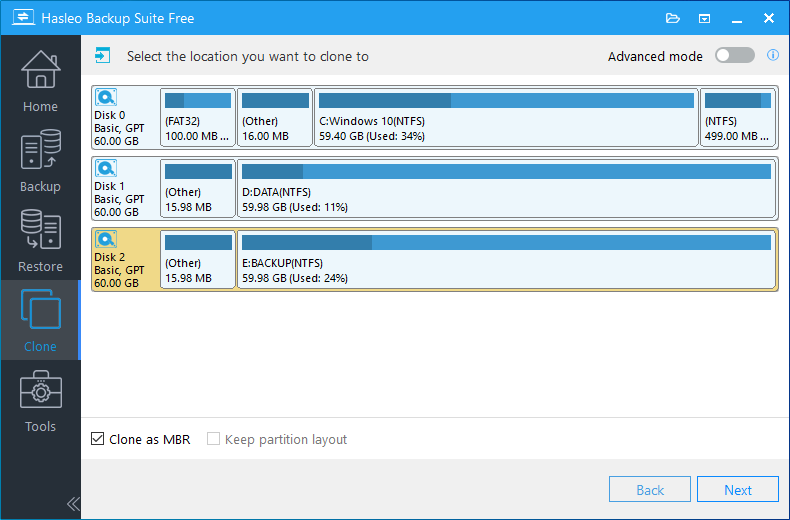
Step 5. Adjust the partition size and location according to your needs, then click "Proceed". The system will pop up a warning message, prompting you that all data on the selected drive will be deleted. Please back up your important data in advance. If you have already backed up your data or do not wish to, click "Yes" to continue.
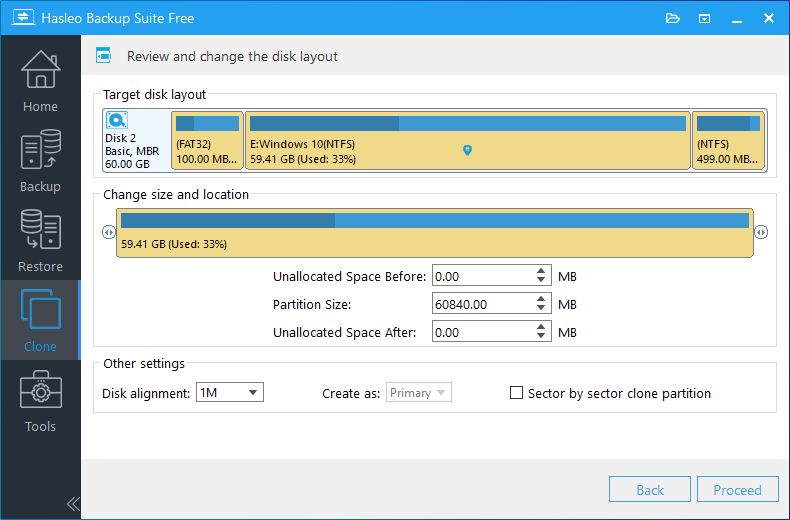
* Disk alignment:
* The Sector by sector clone partiton option copies every sector from the source partition to the destination partition, including unused sectors.
Step 6. Hasleo Backup Suite is now cloning the Windows operating system to the target disk. The required time for this process depends on the size of data being cloned; please be patient.
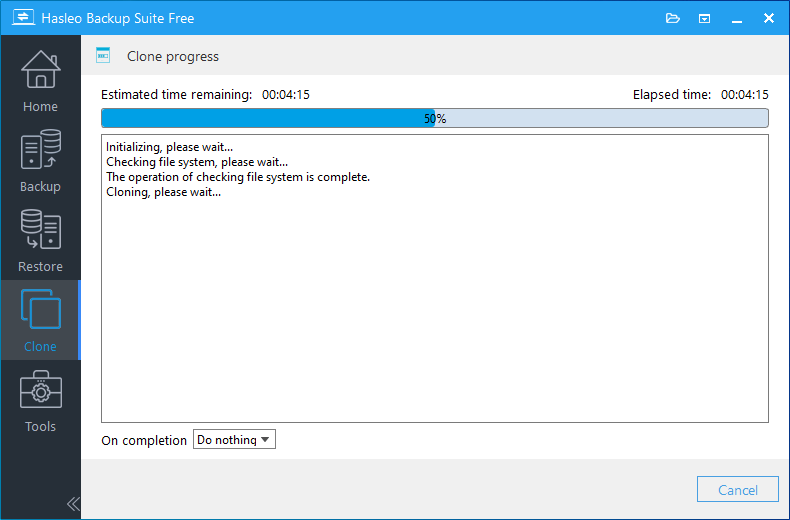
* Here you can specify a power management action to be performed after the backup is complete.
As mentioned above, you can easily clone Windows from a GPT disk to an MBR disk using Hasleo Backup Suite, and you can convert GPT disk to MBR disk with the disk clone feature.
As professional Windows backup and cloning software, Hasleo Backup Suite supports cloning Windows from a GPT disk to an MBR disk, restoring a GPT Windows system backup image to an MBR disk, or cloning Windows from an MBR disk to a GPT disk.